Tagging Record 
What
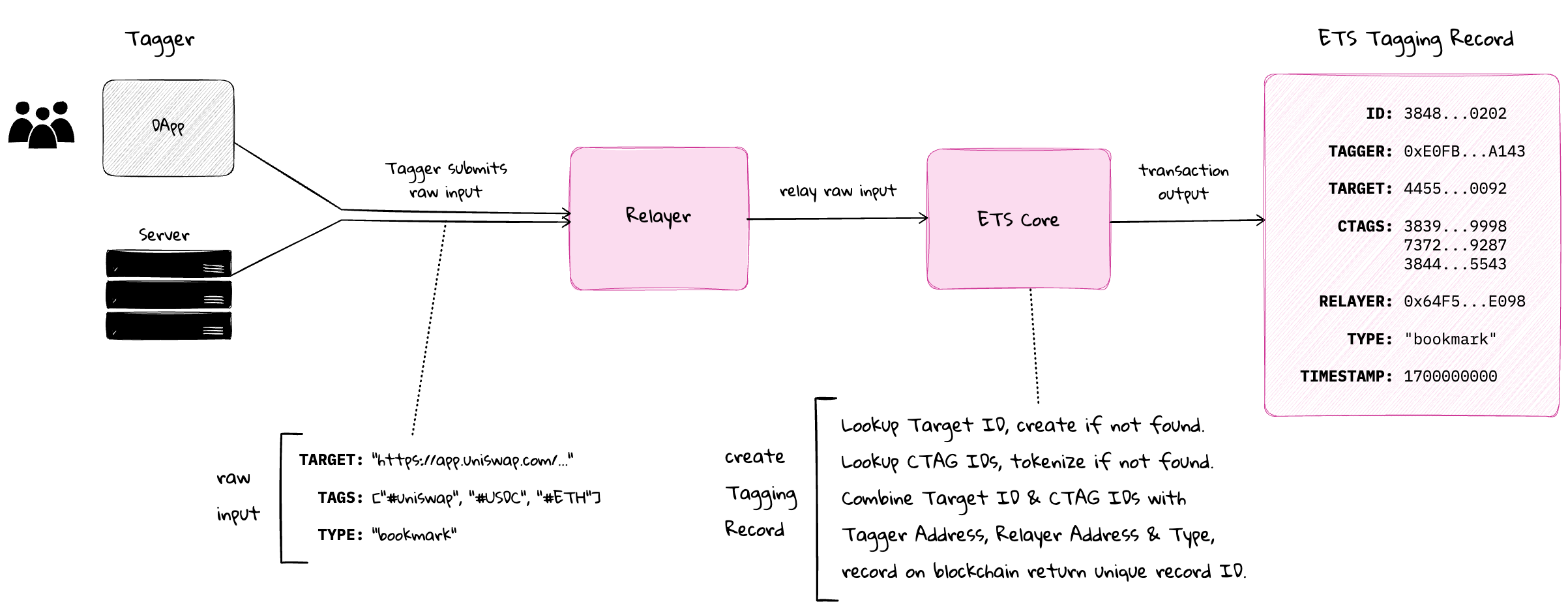
A Tagging Record is the fundamental data structure of ETS that captures the relationship between tags (CTAGs), targets (URIs), and participants (Relayers and Taggers). Each record has a unique ID computed from its composite elements.
Why
Tagging Records enable ETS to:
- Track who applied which tags to what content
- Maintain provenance of tagging actions
- Support multiple tagging contexts through record types
- Enable fee distribution to CTAG owners and relayers
- Create composable on-chain tagging history
How
Tagging Records are created and managed through the ETS core contract through authorized Relayers. These Relayers (contracts themselves) interact with the ETS core contract which manages record creation, modification, and fee distribution to ensure all tagging actions follow protocol rules.
 View Image
View Image1. Data Structure
Tagging Records are stored on-chain as structs containing the essential elements of who tagged what, where and why:
struct TaggingRecord {
uint256[] tagIds; // Ids of CTAG token(s)
uint256 targetId; // Id of target being tagged
string recordType; // Arbitrary identifier for type of record
address relayer; // Address of Relayer contract
address tagger; // Address that initiated tagging
}2. Record ID Generation
Each Tagging Record has a unique ID computed from its composite elements:
taggingRecordId = uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(
targetId,
recordType,
relayer,
tagger
)));This ensures that every tagging event is uniquely identifiable and attributable.
2. Creating Records
- Use
createTaggingRecord()for new records with validated tags and targets - Use
applyTagsWithRawInput()with strings for convenient creation - Use
applyTagsWithCompositeKey()with existing tag/target IDs - Each creation generates a unique record ID and emits event
3. Modifying Records
The following actions can be performed on existing tagging records by the original tagger via any ETS Relayer:
- APPEND: Add additional tags to existing record
- REPLACE: Overwrite existing tags with new set
- REMOVE: Remove specific tags from record
4. Tagging Fees
- ETS charges a protocol-governed fee for each CTAG used in a tagging record
- This fee is also collected when new tags are added to a record via the APPEND action
- No fee is incurred for removing CTAGs from a record
5. Fee Distribution
When these fees are collected:
- Platform receives base percentage
- CTAG's originating Relayer receives commission
- Tag owners receive remaining share