Relayer 
What
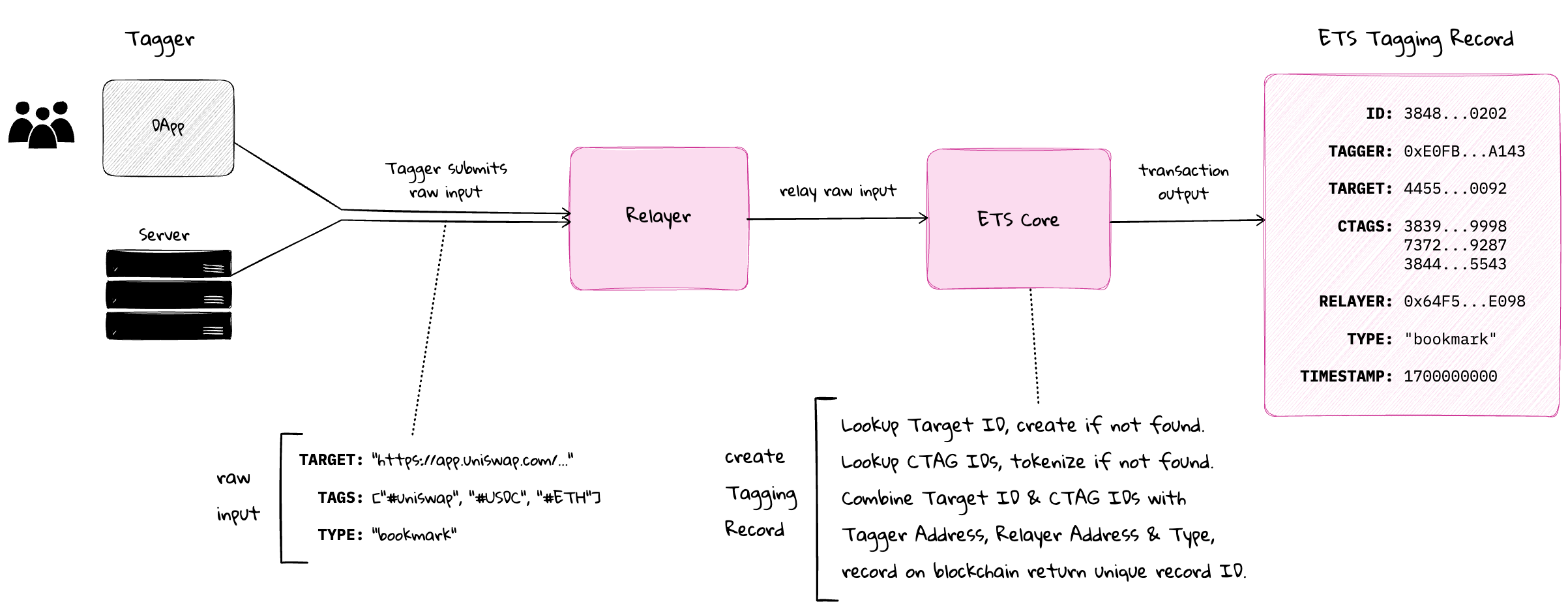
A Relayer is the interface between applications and the ETS core.
 View Image
View ImageWhy
Relayers enable ETS to:
- Provide a uniform, simple tagging interface for applications
- Ensure protocol-compliant tag and tagging record creation
- Ensure the application facilitating the tagging process is credited for its role
- Extend ETS functionality without modifying ETS core
How
Relayers are deployed as upgradeable beacon proxies through the ETS governed ETSRelayerFactory.sol, pointing to ETSRelayerV1.sol. This pattern ensures all Relayers can be upgraded simultaneously while maintaining their unique state and configuration.
1. Creating a Relayer
- Deployer must own at least one CTAG token
- Relayer name must be unique and 2-32 characters
- Only one Relayer allowed per owner address
- Deployer becomes Relayer admin and owner
2. Core Functions
2.1. CTAG & Tagging Record Management
getOrCreateTagIds()- Create new or fetch existing CTAGsapplyTags()- Create or append to tagging recordsreplaceTags()- Overwrite tags in existing recordsremoveTags()- Remove tags from records
2.2. Raw Input Structure
struct TaggingRecordRawInput {
string targetURI; // URI to be tagged
string[] tagStrings; // Array of tag strings
string recordType; // Type of tagging record
}This raw input structure allows applications to interact with ETS core using simple strings rather than pre-computed IDs. See IETS.TaggingRecordRawInput and SDK Core createTaggingRecord().
3. Tagging Fees
ETS charges a protocol-defined fee for each CTAG used in tagging operations. These fees incentivize tag creation, maintain protocol economics, and reward participants in the ETS ecosystem.
3.1 Fee Handling
The Relayer provides a helper function computeTaggingFee() that allows applications to calculate exact fees before transactions, preventing failures. This is especially important when handling multiple tags or complex operations like APPEND and REPLACE actions.
The fee calculation considers:
- Number of new tags being added
- Type of action being performed (new record, append, replace)
- Current protocol-defined fee rate
This design ensures transparent, predictable fee handling while maintaining protocol economics. The Relayer's role in fee management is crucial for both proper protocol operation and good UX in applications using ETS.
// Direct contract interaction
function computeTaggingFee(
IETS.TaggingRecordRawInput calldata _rawInput,
IETS.TaggingAction _action
) external view returns (uint256 fee, uint256 tagCount);// Using ETS SDK
const [fee, tagCount] = await relayer.computeTaggingFee(
{
targetURI: "https://example.com",
tagStrings: ["#Example", "#Test"],
recordType: "bookmark"
},
TaggingAction.APPEND
);
// Apply tags with computed fee
await relayer.applyTags([rawInput], { value: fee });Future Extensions
The Relayer's upgradeable design makes it our primary focus for expanding ETS functionality. As detailed in our roadmap, planned extensions include:
- Dynamic fee structures based on market conditions
- Relayer-sponsored tagging fees for improved UX
- Pluggable access controls for custom restrictions
- Cross-chain tagging capabilities
These features will be implemented through Relayer upgrades, allowing applications to access new functionality without changes to ETS core contracts.