CTAG Auction 
What
The ETS Auction is a continuous English-style auction mechanism for distributing CTAGs. A fixed number of CTAGs is always up for auction, and when each auction ends, a new one automatically begins. Each auction runs for a fixed duration but may be extended in the final moments by new bids.
Why
The auction system enables ETS to:
- Distribute CTAGs fairly to the community
- Control the rate of CTAG distribution through max number of concurrent auctions
- Establish market for CTAGs
- Generate revenue for protocol participants
- Prevent namespace squatting
- Create an engaging community dynamic
How
Auctions are managed through the ETSAuctionHouse.sol contract. The design of the auction is inspired by the Nouns DAO auction.
Default Auction Settings
| Parameter | Variable | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Concurrent Auctions | maxAuctions | 3 | Number of simultaneous auctions |
| Duration | duration | 24 hours | Length of each auction |
| Time Buffer | timeBuffer | 15 minutes | Extension period for late bids |
| Min Bid Increment | minBidIncrementPercentage | 5% | Minimum increase over previous bid |
| Reserve Price | reservePrice | 0.1 ETH | Minimum first bid amount |
Auction Structure
struct Auction {
uint256 auctionId; // Incremented auction number
uint256 tokenId; // CTAG being auctioned
uint256 amount; // Current highest bid
uint256 startTime; // Auction start time
uint256 endTime; // Scheduled end time
uint256 reservePrice; // Minimum first bid
address payable bidder; // Current highest bidder
address payable auctioneer; // Defaults to ETS
bool settled; // Whether auction is settled
}Bidding
- Auction begins with first bid
- First bid must meet reserve price
- Subsequent bids must increase by minimum percentage
- Late bids extend auction by time buffer
- Bids must be in native currency (ETH)
Note The auction extension mechanism ("time buffer") prevents last-second sniping by adding time when late bids are placed.
Settling an Auction
- Auction must be ended to settle
- Any address can settle auction
- Winning bidder receives CTAG
- Proceeds distributed to:
- Platform treasury
- Tag creator
- Originating relayer
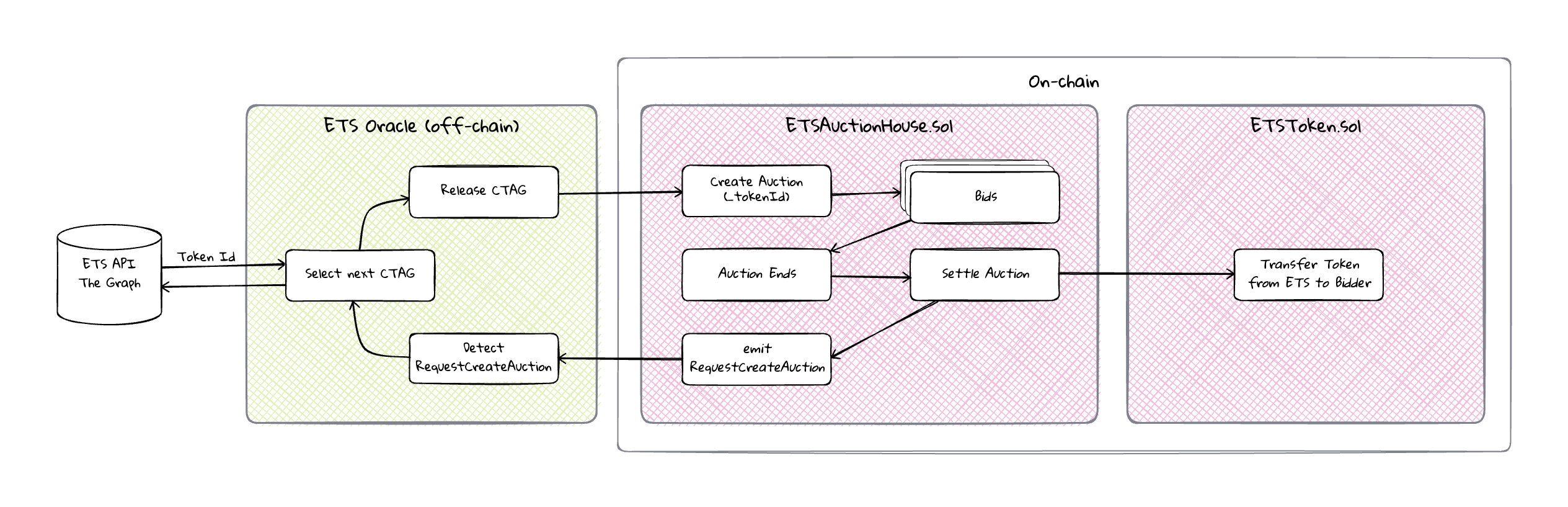
Auction Oracle
 View Image
View ImageThe ETS Auction Oracle is an off-chain process that monitors the ETS Auction House and selects the next CTAG to be released for auction. The Oracle is responsible for:
- Detecting
RequestCreateAuctionevent, which is emitted when an auction is settled - Selecting CTAG with the highest use count (eg. used in most Tagging Records)
- If CTAGS have the same use count, the oldest CTAG is selected
- "Releasing" next CTAG for auction via on-chain transaction
Revenue Distribution Model
When an auction is settled, the proceeds are automatically distributed between three key participants:
| Participant | Variable | Default % | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tag Creator | creatorPercentage | 40 | Rewarded to the original creator of the CTAG |
| Relayer | relayerPercentage | 30 | Rewarded to the relayer that supported the creation of the CTAG |
| Platform Treasury | platformPercentage | 30 | Allocated to ETS protocol treasury |
The distribution works as follows:
- The total auction amount is split according to the percentage allocations
- Each participant's share is tracked in an
accruedbalance - Participants can withdraw their accrued balance at any time using the
drawDown()function - The system maintains a record of lifetime earnings through the
paidmapping
This model incentivizes:
- Tag creators to submit high-quality tags that get used frequently
- Relayers to support tag and tagging record creation
- Sustainable protocol revenue for ongoing development
The percentage splits are governed by the community and can be adjusted through the admin functions setProceedPercentages().